Introduction:
A temporary structure on the
outside of a building, made of wooden planks and metal poles, used by workmen
while building, repairing, or cleaning the building.
It is temporary
elevated structures build to enable man and material (Machinery) to perform
work at height.
A Temporary
platform, either supported from below our suspended from above, on which
workers sit or stand when performing tasks at height above the ground.
In terms of the basic structure
of scaffolding, the three main components are the
standards (the vertical scaffold poles that bear the weight of
the scaffolding), the ledgers (the horizontal poles that attach to
each standard), and transoms (main transoms are attached at 90 degrees to
ledgers adjacent to the standards.
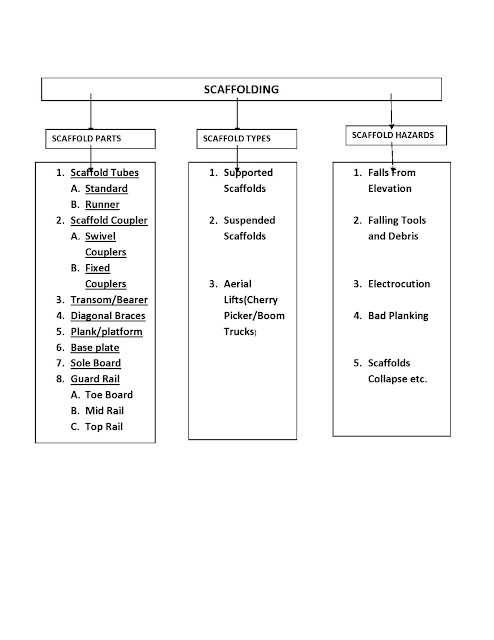
Scaffold Parts:
ANY WORK ABOVE 6FT OR 2MTR. REQUIRED SCAFFOLDS
Components of scaffolds
1) Sole boards quality base plate.
2) Vertical Bar
3) Horizontal bar
4) Ladder
5) The Board
6) Wooden Planks
7) Couplers – Double, Swivel, Universal, Pin
8) Mid rail, Top rail, Guard rail.
Scaffold Tubes
Scaffold tubes
or pipes, are manufactured out of either steel or aluminium. Aluminium pipes,
while lighter, are not as strong as steel scaffold tubes, and are therefore not
recommended for any long-term or heavy-duty usage. Steel scaffold tubes are
highly recommended for anything more than very light, low-level, and non-weight
bearing usage.
Scaffold tubes are generally made of aluminium or steel though there is composite scaffolding that utilises fibril-wound tubes of glass fibre in a polyester or nylon matrix due to the high cost of composite tube, which is normally used only when there is a danger from overhead electric cables that can’t be cut off.
Scaffold tubes are generally made of aluminium or steel though there is composite scaffolding that utilises fibril-wound tubes of glass fibre in a polyester or nylon matrix due to the high cost of composite tube, which is normally used only when there is a danger from overhead electric cables that can’t be cut off.
Scaffold Couplers
Other
scaffolding components, such as couplers, are often made from either
drop-forged steel, or pressed steel, both of which materials produce highly
durable components which, when installed by competent individuals, are easily
capable of withstanding very high workload.
Couplers are fittings that hold the tubes together. The most familiar are known as scaffold couplers and there are three basic types, which are Putlog Couplers, Right-angle Couplers and Swivel Couplers.
Ledgers, Standards and Transoms
In terms of
the basic structure of scaffolding, the three main components are the standards
(the vertical scaffold poles that bear the weight of the scaffolding), the
ledgers (the horizontal poles that attach to each standard), and transoms (main
transoms are attached at 90 degrees to ledgers adjacent to the standards,
intermediate transoms are attached at set distances apart 90 degrees to the
angle of the ledgers and are used to provide support for scaffold boards).
Adjustable Base Plates
You can select from different height-adjustable base plates that come with strong and self-cleaning round threads to adjust to the ground. It comes with colour and notch markings to render safeguard against over-winding.
Diagonal Braces
The diagonal braces with wedge locks further support the basic structure comprising of vertical standards and ledgers. Additionally, their high connection standards assist special structures.
Toe boards
Toe boards must be used at the end of the scaffolding to ensure
that materials and tools do not fall off the scaffold. The toe boards must
be a minimum height of 150mm. The boards also prevent the possibility of
people slipping off the edge of the platform. Toe boards may be removed to
allow access for materials and workers, but must be replaced
immediately afterwards.
Between
vertical standards, toe boards are placed. Toe boards are obtainable in
aluminium, steel or wood. The toe board of steel lowers the fire hazard and
also lasts long. Because of its design, there are no openings or gaps between
the deck and the toe board.
Decks
Decks are also referred as planks and they are available in aluminium, aluminium frame with plywood board and hot-dip galvanised steel. Decks are a structural component and so ledgers aren’t needed at the deck level, which not only saves cost but also weight.
TYPES OF SCAFFOLDS:

1) Suspended Scaffolds:
The suspended or
swing stage scaffold can be either raised or lowered as it has a suspended
platform. These types are commonly associated with the type’s windows washers.
It is platform
suspended by ropes or other non-rigid, overhead support.
Types of suspended scaffold :-
a)
Single Point :-
A
single point scaffold consists of a platform suspended by one rope from and
overhead support and equipped with means to permit the movement of the platform
to desired work levels. The most common among these is the scaffold used by
window washers to clean the outside of a skyscraper (also known as a
boatswain’s chair).
b)
Two Point / Double Point ( Swing Stage ) :-
Double point from supported by hanger (Stirrups) suspended by two ropes from over head supported and equipped with a means two permit the plat from to be raised and lowered.
C) Multi – Point Adjustable:-
Platform suspended by more than
two ropes from overheads support and equipped with a means to permit the
platform to be raised and lowered.
D)
Multi Level:-
Two
point and multi point adjustable suspension scaffold with series of platform at
various level resting on common stirrups.
2) Supported
Scaffolds:-
Supported scaffolds consist of
one or more platforms supported by outrigger beams, brackets poles, legs
upright, posts frames or similar rigid support.
1. Trestle Scaffolding.
The working platform is supported on
movable ladders or tripods in trestle scaffolding. It is used up to a height of
5m and is normally used for work inside the room like repairs, paintings and
likewise.
2. Steel
Scaffolding
Steel scaffolding is made from steel
tubes that are set jointly by steel fittings or couplers. It is simple to erect
and to dismantle. It has better robustness, greater durability and superior
fire resistance. Though it is not affordable cost wise, it provides greater
safety for workers. That’s the precise reason it is used so widely these days.
3.
Patented Scaffolding:
Patented scaffolding are also made from
steel; however, they are fitted with special couplings and frames etc. These
are ready made scaffolding that are obtainable on the market. Working platform
is set on the brackets that are adjustable to the required level in this type
of scaffolding.
4.
Suspended Scaffolding:
Suspended scaffolding is mainly used for
paintings, repair works, etc. Here, with the assistance of chains or wire ropes
etc., the working platform is suspended from roofs. It can be lifted or lowered
to the desired level.
In cantilever scaffolding, the standards
are supported by a chain of needles and these needles are pulled out via holes
in the wall. This is known as “single frame” scaffolding-type. In another type,
needles are supported inside the floors via the openings and this is called
independent or double frame scaffolding type. When constructing cantilever
scaffolding, good care should be taken. Normally, under below mentioned
conditions, cantilever scaffolding is used.
- .When the upper part of the wall is under
construction
- .When ground is close to the wall and is
free from traffic
- When the ground is not capable of supporting standard.
- 6.Single Scaffold:Single scaffolding is usually used for brick masonry and so it is also known as brick layer’s scaffolding. Single scaffolding comprises of standards, putlogs, ledgers etc., which corresponds to the wall at a distance of around 1.2 m. Distance amongst the standards is around 2 to 2.5 m. Ledgers join the standards at an upright gap of 1.2 to 1.5 m. Putlogs are extracted from the gap remaining in the wall to one end of the ledgers. Putlogs are positioned at a gap of 1.2 to 1.5 m.
7.
Double Scaffolding:
Double Scaffolding is normally used for stone masonry job, therefore, it is also known as mason’s scaffolding. It is also known as the independent scaffolding. Typically, in stone walls, it is tough to make holes in the wall for supporting putlogs; thus, two scaffolding rows are made to make it robust. Basically, the first row is about 20 to 30 cm away from the wall, and another one is 1m away from the first row. Then after putlogs are positioned that are supported by both the frames. In order to make it sturdier, cross braces and rakers are supplied.
Double Scaffolding is normally used for stone masonry job, therefore, it is also known as mason’s scaffolding. It is also known as the independent scaffolding. Typically, in stone walls, it is tough to make holes in the wall for supporting putlogs; thus, two scaffolding rows are made to make it robust. Basically, the first row is about 20 to 30 cm away from the wall, and another one is 1m away from the first row. Then after putlogs are positioned that are supported by both the frames. In order to make it sturdier, cross braces and rakers are supplied.
Frame scaffold or fabricated frame :-
Platform
supported on fabricated end frames with integral posts horizontal bearers and intermediate
members.
Tube and Coupler:-
Platform supported by tubing,
erected with coupling devices connecting upright. Braces bearers and
runners.
Pole:-
Posts with fixed connection
point that accept runner’s bearers and diagonals that can be interconnected at
predetermined levels.
Mobile:-
It is portable unpowered or
wheel mounted supported scaffold.
Note :-
- Scaffolds and scaffold components must be capable of supporting without failure, their own weight and at least 4 times their maximum intended load.
- Each suspension rope must be capable of supporting without failure at least 6 times the maximum intended load.
- Aerial Lifts – such as cherry pickers or boom
trucks.
Same important of Point :-
1) Guardrails and toe boards shall be installed
on all open sides and ends of platforms more than 10 feet above the ground and
floor, except needle beam scaffolds.
2) Scaffolds 4 feet to 10 feet in height, having
a minimum horizontal dimension in either direction of less than 45 inches shall
have standard guardrails installed on all open sides and ends of the platforms.
3) Guardrails shall be 2*4 inches or the
equivalent approximately 42 inches high, with a midtrial, when required.
4) Supports shall be at intervals not to exceed 8
feet.
5) Toe boards shall be a minimum of 4 inches in
height.
Capacity
of scaffolds
1) Heavy duty scaffolds 750lbs.
2) Medium duty scaffolds 500lbs.
3) Light duty scaffolds 250lbs.
Tags
of scaffolds
Red
– Unsafe – Do not use
Green
– safe – for use
Yellow
– Fall protection required
Hazards
in scaffolding:-
Falls
from elevation :- Caused by slipping unsafe access and the lack of fall protection.
This is the most common scaffolding hazard. Preventing falls from
heights, the Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA) requires that proper
fall protection be placed on all scaffolds suspended over 10 feet above ground.
A personal fall arrest system or a guardrail system must be utilized at all
times.
1) Bad planking:
Another cause of scaffold-related incidents is unsecured planking. When planks are uncleated or not secured enough, they might slip off and cause the worker to fall. Planks also have tendency to break if overloaded or in poor condition that is why it is important that proper grades of lumber is used and that planks are inspected thoroughly. Another problem related to planks is insufficient or excessive overhang. When a worker stands on a overhanging position, this may tip up and cause a fall.
2) Getting struck by falling tools or debris:
More often than not, scaffolding-related injuries involve being struck with falling debris. This is why guardrails are an important component of scaffold construction, not only to protect the worker from falling but also to prevent any material from falling off a scaffold and hitting people below.
3) Electrocution:
Many times workers one injured because of electrical shock from overhead power lines. Electricity is a major risk when it comes to using scaffolds since electrical lines are usually elevated making the scaffold user prone to contact with such lines. Safety standards require scaffolds and workers to maintain a secure clearance from power lines. Ideal clearance is 10 feet if the voltage is less than 50 kV (kilovolts) and more than 10 feet and 4 inches for every 1 kV over 50 kV.
4) Scaffold collapse:
Due to overloading of man and machinery and end stability many times, chances of scaffold collapse, worker scan injured.
5) Behavioral Hazards:
Worker should never rid on scaffolding while it is being moved. Movable scaffolding should not be occupied unless the wheels are securely locked end place.
6)Atmospheric Hazards:
Workers on scaffolding are in danger if they are working in stormy or high wind conditions.
7)Slippery Surfaces:
Workers should avoid working on slippery scaffolding in ice, snow or mud. They should clean up and chemical, food or grease spills immediately.
1) Bad planking:
Another cause of scaffold-related incidents is unsecured planking. When planks are uncleated or not secured enough, they might slip off and cause the worker to fall. Planks also have tendency to break if overloaded or in poor condition that is why it is important that proper grades of lumber is used and that planks are inspected thoroughly. Another problem related to planks is insufficient or excessive overhang. When a worker stands on a overhanging position, this may tip up and cause a fall.
2) Getting struck by falling tools or debris:
More often than not, scaffolding-related injuries involve being struck with falling debris. This is why guardrails are an important component of scaffold construction, not only to protect the worker from falling but also to prevent any material from falling off a scaffold and hitting people below.
3) Electrocution:
Many times workers one injured because of electrical shock from overhead power lines. Electricity is a major risk when it comes to using scaffolds since electrical lines are usually elevated making the scaffold user prone to contact with such lines. Safety standards require scaffolds and workers to maintain a secure clearance from power lines. Ideal clearance is 10 feet if the voltage is less than 50 kV (kilovolts) and more than 10 feet and 4 inches for every 1 kV over 50 kV.
4) Scaffold collapse:
Due to overloading of man and machinery and end stability many times, chances of scaffold collapse, worker scan injured.
5) Behavioral Hazards:
Worker should never rid on scaffolding while it is being moved. Movable scaffolding should not be occupied unless the wheels are securely locked end place.
6)Atmospheric Hazards:
Workers on scaffolding are in danger if they are working in stormy or high wind conditions.
7)Slippery Surfaces:
Workers should avoid working on slippery scaffolding in ice, snow or mud. They should clean up and chemical, food or grease spills immediately.
1) Check Permit.
2) Inspect the tag for sigh & time.
3) Fall protection system must be used if men are
working above 6ft.
Competent
Person:-
Competent person as one who is
capable of identifying existing and predictable hazards in the surrounding or
working conditions.
Duties of Competent Person:-
Duties of Competent Person:-
1) Determine if it is safe for employee to work
on scaffold during storms or high winds.
2) Train employees involved in erecting
disassembling moving operating preparing maintaining or inspecting scaffolds.
3) Inspect scaffold for visible defects before
each work shift and after any occurrence which could affect the structural
integrity.
4) Inspect ropes being used for Top rails and mid
rail.
5) Inspect ropes on suspended scaffold prior to
each work sheet.
6) Deter mind feasibility and safety of providing
fall protection
(Thanking you)